Understanding Spatial Filters
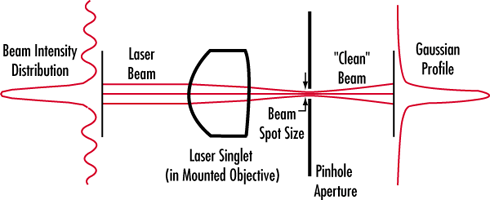
Spatial Filters are designed to be used with lasers to "clean up" the beam. Often times a laser system does not produce a beam with a smooth intensity profile. In order to produce a clean Gaussian beam, a spatial filter is used to remove the unwanted multiple-order energy peaks and pass only the central maximum of the diffraction pattern (see illustration). Also, when a laser beam passes through a system, dust in the air or on optical components can disrupt the beam and create scattered light. This scattered light can leave unwanted ring patterns in the beam profile. The spatial filter removes this additional spatial noise from the system. The spatial filter assembly consists of a microscope objective, a pinhole aperture, and a positioning mechanism. The positioning mechanism has precision X-Y movements that center the pinhole at the focal point of the objective lens. Our TECHSPEC® Laser Objectives are designed for HeNe lasers (632.8nm) and provide the smallest spot sizes possible. Choosing the correct pinhole and objective combination will yield optimal results. The following equations were used to determine the values for the Aperture Selection Chart.
Equation 1.0 Beam Spot Diameter (microns) = (1.27 * λ * f) / D
Where:
λ = wavelength of laser (microns)
f = focal length of objective lens (mm)
D = input beam diameter (mm)
Equation 2.0 Pinhole size is then determined for the table (see note):
Pinhole Diameter (microns) = 1.5 * Beam Spot Size Diameter (microns)
Note: The factor of 1.5 in Equation 2.0 is determined as the optimal factor in order to pass the maximum amount of energy, while eliminating as much spatial noise as possible.
Aperture Selection Chart | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
EFL of Microscope Objective Lens (mm) | 5.5mm | 8.0mm | 8.5mm | 9.0mm |
0.96mm Input Beam Dia. | 8μm | 10μm | 12.5μm | 12.5μm |
0.81mm Input Beam Dia. | 8μm | 12.5μm | 12.5μm | 15μm |
0.75mm Input Beam Dia. | 8μm | 12.5μm | 15μm | 15μm |
0.70mm Input Beam Dia. | 10μm | 15μm | 15μm | 15μm |
0.68mm Input Beam Dia. | 10μm | 15μm | 15μm | 15μm |
0.63mm Input Beam Dia. | 10μm | 15μm | 15μm | 15μm |
0.48mm Input Beam Dia. | 12.5μm | 20μm | 20μm | 25μm |
版權(quán)所有 © 2025 江陰韻翔光電技術(shù)有限公司 備案號(hào):蘇ICP備16003332號(hào)-1 技術(shù)支持:化工儀器網(wǎng) 管理登陸 GoogleSitemap