Successful Light Polarization Techniques
Video and machine vision systems rely on electronic imagers that typically exhibit anywhere from eight-bit to twelve-bit signal-to-noise ratio. Although sufficient for many applications, cameras in this category may be problematic in cases where the field of view includes extremely bright regions or hot spots. Some objects have certain features that are extremely reflective, or objects may be illuminated from an angle that produces intense reflection. Light polarization filters offer solutions to these and other common imaging problems.
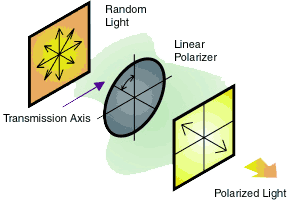
Understanding Polarization Axis
By considering light as an electromagnetic wave, we realize that in three-dimensional space a wave can oscillate up and down, side to side, or anywhere in between. Incandescent, fluorescent, LED, and many laser light sources are randomly polarized. In other words, the oscillating angle or plane of light from each point on the light source is varying with time. Taken as a time average, therefore, randomly polarized light sources continuously output all angles of polarization.
Polarizers absorb incident light oscillating in all but one plane - its polarization axis - yielding linear polarization. Another example of polarization is the partial polarization of light reflecting from a plane surface, an effect less dramatic than a polarizer element. Linear polarization of a randomly polarized light source reduces the intensity of the source theoretically by 50%, and in practice closer to 60-65%. Light that passes through two polarizers with orthogonal polarizing axes will be compley attenuated. However, the almost total elimination of hot spots and glare is exactly what makes a polarizer effective in evening out illumination levels within a field.
Application Examples
Shown are examples of some common polarization of light techniques used in imaging applications. By utilizing a linear polarizer over the light source, the lens, or both, it is possible to eliminate glare from a reflective surface, bring out surface defects or show stress in a transparent object. More detailed information on which type of polarizer is right for your application can be found in our Polarizer Selection Guide.
Eliminating Hot Spots: Hot spots are highly reflective areas within a more diffuse reflecting field. Polarizing the light that strikes these reflective areas, and using a crossed polarizer over the lens, effectively eliminates the hot spots, while evenly illuminating the rest of the field.


Without Polarizer Polarizers over Light Source and Lens
Glare From a Plane Surface: Glare from highly reflective surfaces or optical windows is removed by putting a polarizer over the lens. Due to partial polarization of light, the light source may or may not require a polarizing filter in this scenario.


Without Polarizer Polarizer over Light Source or Lens
Contrast Enhancement: Ring light guides are popular for their even, diffuse illumination. However, glare or reflection of the ring itself may occur. Polarizing the ring output and the lens separay can reduce these effects, and bring out surface details.


Without Polarizer Polarizers over Ring Light and Lens
Stress Evaluation: Stress, or unwanted refractive index variations, causes a rotation in the angle of polarization. Viewing an unstressed clear object between crossed polarizers should yield a compley dark field. However, when stress is present, the localized changes in refractive index actually rotate the angle of polarization to give varying degrees of transmission - even different amounts of transmission for different colors.

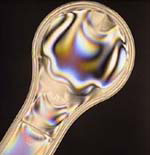
Without Polarizer Polarizers Before and After Transparent Object
版權(quán)所有 © 2025 江陰韻翔光電技術(shù)有限公司 備案號(hào):蘇ICP備16003332號(hào)-1 技術(shù)支持:化工儀器網(wǎng) 管理登陸 GoogleSitemap